Blob-like + Non-encrusting
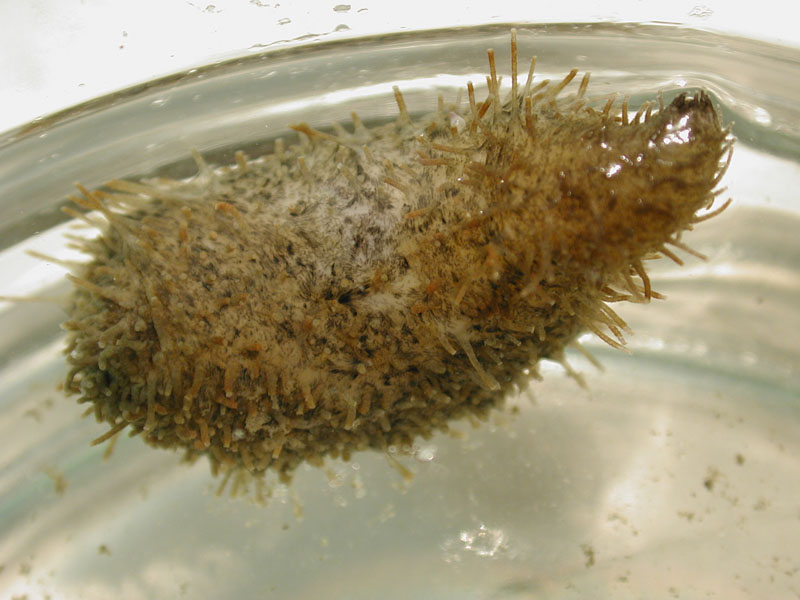
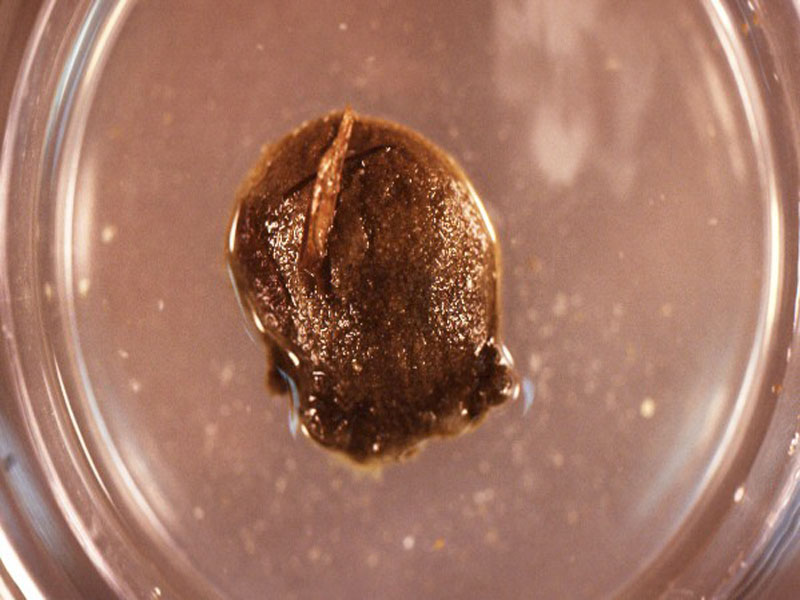
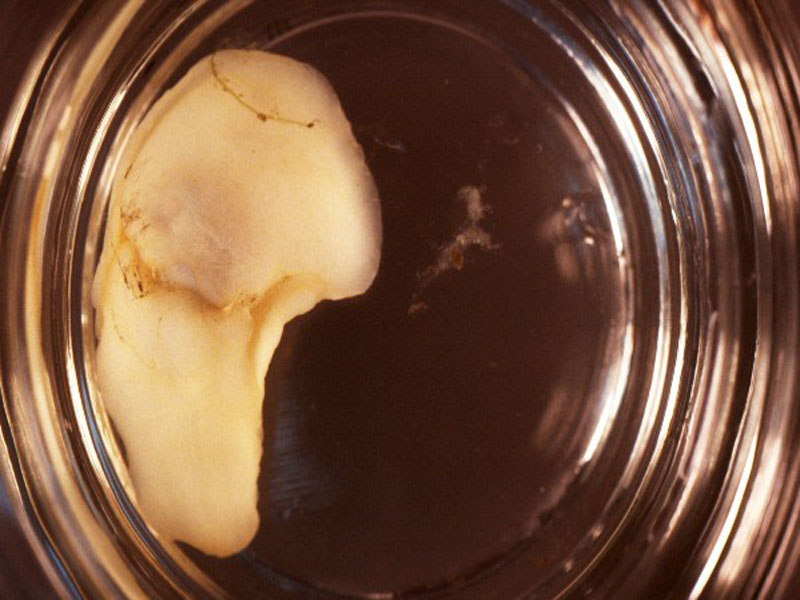
Hairy Cucumber, Mexican Thyone
Description
Similar to the brown cucumber, the hairy cucumber is found in subtidal, seagrass beds of the Gulf and Caribbean. Growing only to 2 inches long, it has grayish podia (feet) scattered all over its body with only those on the lower surface having suckers.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This sea cucumber is a detritivore, meaning that it feeds on organic wastes. In doing so, it can consume clam feces and pseudofeces, removing these wastes from the clam bag.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
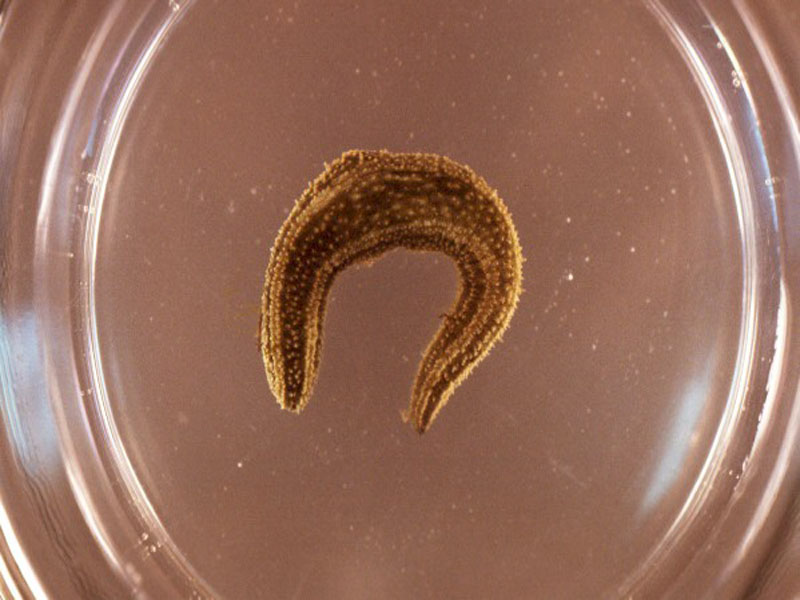
Mottled Sea Hare
Description
The mottled sea hare is found in seagrass beds and protected sand flats of shallow waters where macro algae (sea grasses) are abundant. This swimming species is extremely variable in color, with the background color varying from yellow brown, brown gray, green or black, and is relatively large, growing up to 10” long. Sea hares are so called because of the fancied resemblance of the second pair of antennae to a hare's long ears, and the similarity of the animal's general shape to that of a crouched hare. Like their namesakes, sea hares are herbivorous, eating eelgrass and a variety of red, green, and brown algae from whose pigment they derive their color. An interesting feature is that they emit a cloud of purple mucus when disturbed.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This large “shell-less”snail has a voracious appetite for sea lettuce and can help keep clam bags free of macro algae.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
Taxonomy
- Kingdom:Animalia
- Phylum: MOLLUSCA
- SubPhylum:
- Class: Gastropoda
- Order: Anaspidea
- Family: Aplysiidae
- Genus: Aplysia
- Species: brasiliana
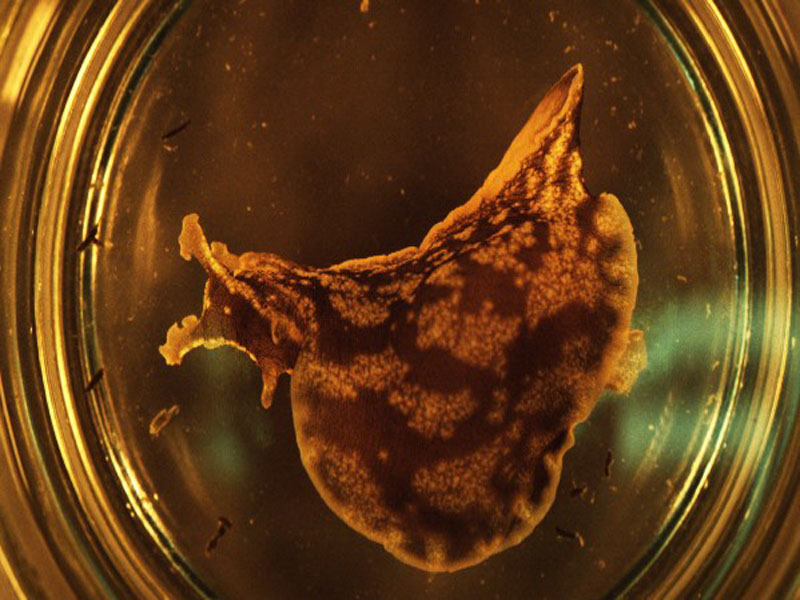
Ragged Sea Hare
Description
The ragged sea hare is a soft, flabby, plump snail, with adults having no shell at all. Found from the Gulf of Mexico to the Caribbean in grassy areas of shallow, protected waters, it grazes on macro algae within the grassy areas, and lays its eggs in large, tangled masses of spaghetti-like strings. This swimming snail has a green-grey to olive-green color with white specks and is covered in highly branched filaments. When handled or disturbed, the ragged sea hare, like other sea hares, gives off a deep purple ink. It reaches 4 inches in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This is large “shell-less” snail that has an appetite for green macro algae and can help keep clam bags free from fouling.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
Humans
Description
Humans are bipedal (two-legged) apes belonging to the great ape family. Humans have a highly developed brain capable of abstract reasoning, language, and introspection. This, combined with an erect body carriage that frees their upper limbs for manipulating objects, allows them to make greater use of tools than any other species. Like most primates, humans are by nature social. However, humans are particularly adept at utilizing systems of communication for self-expression and the exchange of ideas. Humans inhabit every continent with a total population of over 6.5 billion people as of 2006.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
First and foremost, humans are consumers of clams, and purchase clams grown by farmers for consumption. Humans live in coastal areas, often in sight of clam aquaculture leases. Their activities on land, such as waste disposal, placement of dwellings (zoning density), and use of fertilizers and pesticides, can affect the quality of inshore waters, the management plan of the shellfish harvesting area, and the safety of shellfish for human consumption. Humans also use inshore coastal waters for boating, fishing and recreational activities, as well as other commercial activities, such as crabbing. Sometimes these activities can cause problems for clam farmers and their crops. In particular, clam bags can be cut by a motor’s propeller when a boater runs over a lease at low tide. Further, some growers use SCUBA or hookah rigs to work their crops on high tides or on deeper leases. Unaware boaters could potentially snag this equipment causing harm to the diver. Finally, one of the biggest predators of clams is human. Losses of cultured clams from theft can be significant.
- FRIEND, FOE, NEIGHBOR
- Competitor
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Education is the key. To increase consumption of clams, a clam farmer, as well as wholesalers and retailers, must provide information to the public about the nutritional value of clams and tips on how to store, handle, and prepare clams. Marketing brochures and recipes are available through the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services, Bureau of Seafood and Aquaculture Marketing. <HYPERLINK TO http://www.fl-seafood.com/recipes/clam_recipes.htm>. A clam farmer must educate their neighbors as to the economic and environmental importance of clam farming to ensure land use regulations and practices are favorable to maintaining and preserving water quality standards for shellfish harvesting. A clam farmer must also educate boaters, informing them of the location of lease areas as well as the activities conducted on their farms. Educational signs placed at marinas, boat ramps, and on aquaculture lease markers can be used to provide appropriate warnings to the public. Further, growers must display a Diver-Down flag when using SCUBA gear or hookah rigs on their leases. Although control of human predators is problematic, cultured clams are protected by state law (Chapter 812.014, Florida Statues). Stealing of clams is grand theft of the third degree and a felony of the third degree. Some clam farmers must employ security measures, such as continuous surveillance, in order to prevent significant losses due to theft. The Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services provides a reward of up to $2,500 for information leading to the arrest and conviction of individuals unlawfully possessing or harvesting cultured shellfish. Violations are to be reported to 1-800-DIAL-869.

Taxonomy
- Kingdom:Animalia
- Phylum: CHORDATA
- SubPhylum: Vertebrata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primata
- Family: Hominidae
- Genus: Homo
- Species: sapiens
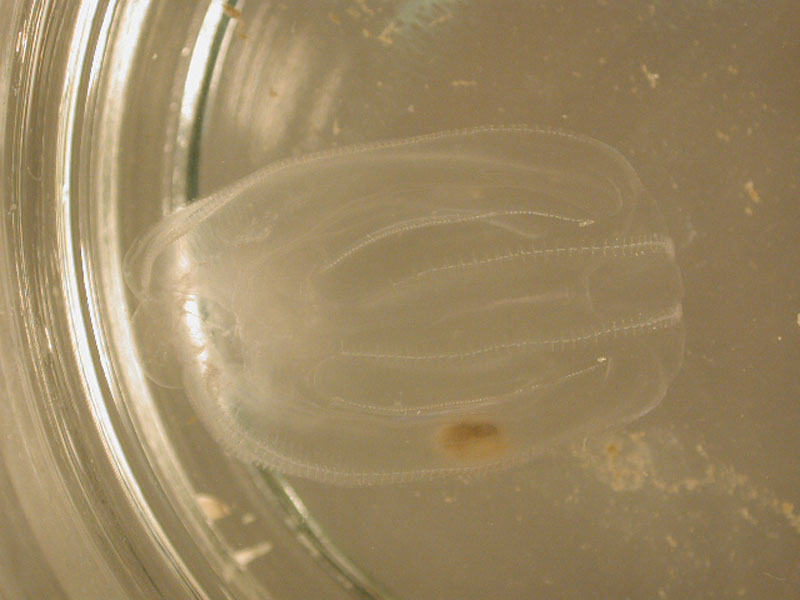
Sea Walnut, Comb Jelly
Description
Despite its name, the comb jelly, or sea walnut, is not a jellyfish, as it is in a phylum all its own. It is comprised of two oval lobes with two small tentacles, and appears transparent. It is lined with four rows of cilia along the body, which help it move through the water. The cilia appear iridescent during the day and luminescent at night. The comb jelly is indigenous to Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico estuaries and inshore waters, though was recently introduced to the Black and Caspian Seas via ballast tanks of ships. Being a voracious predator of zooplankton, fish eggs and larvae, the comb jelly has had a catastrophic effect on the Black and Caspian Sea ecosystems. They are hermaphroditic, bearing both male and female organs, and have the capability of self fertilizing. The comb jelly can grow up to 4 inches in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The comb jelly is rarely found in clam bags, but during the warmer months these animals can be found in "bloom" or large numbers that can greatly reduce the amount of zooplankton (microscopic animals) in the water column. When this happens, there is more phytoplankton (clam food) available for clams.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
Sandy Sea Squirt
Description
The sandy sea quirt is a mud or sand colored solitary tunicate, commonly found along Florida and the Gulf of Mexico coasts. It is usually covered in mud or sand engrained into the animal, making it feel like sandpaper and resembling a ball of sand. The tunic, or thick tissue covering the sea squirt is tough and wrinkled while the mantle tissue is bright orange at the siphons. The incurrent and excurrent siphons are not spaced very far apart, and are used to filter plankton out of the water and bring oxygenated water into the respiratory organs. When picked up and squeezed, they release water from their excurrent siphon in a tight stream, thus the name “sea squirt.” Tunicates are primitive chordates, making them more closely related to humans than any other invertebrates. They can reach 2.5 inches in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Sea squirts (tunicates) are filter or suspension feeders and can compete for the same type of food (micro algae) as clams. This tunicate does not attach to a surface; rather it settles inside a clam bag, usually before the bag is completely buried.
- FOE
- Competitor
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Although these animals can compete with clams for food, they are generally not found in high enough numbers to cause a problem. No practical control method is necessary.
Sea Onion
Description
The sea onion is a sea anemone that ranges from New England to the Gulf of Mexico. It is a burrowing anemone, found in coastal sandy areas, and can burrow up to 14 inches into the sand using a ventral attachment disk. It is translucent, with white longitudinal stripes running along the body. It contains up to 180 tentacles, brown in color due to the presence of zooxanthellae (one-celled plants that live inside cells and tissues of various invertebrates). Often only the short tentacles can be seen, used to catch drifting plankton. If disturbed, it will puff up into an onion-shaped mass and drift with the current to a new location.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Although this anemone is a filter feeder and can potentially compete with clams for food, it most likely catches larger planktonic organisms than clams. It is rarely found in numbers high enough to cause a problem.
- FOE
- Competitor
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No practical control method is necessary.
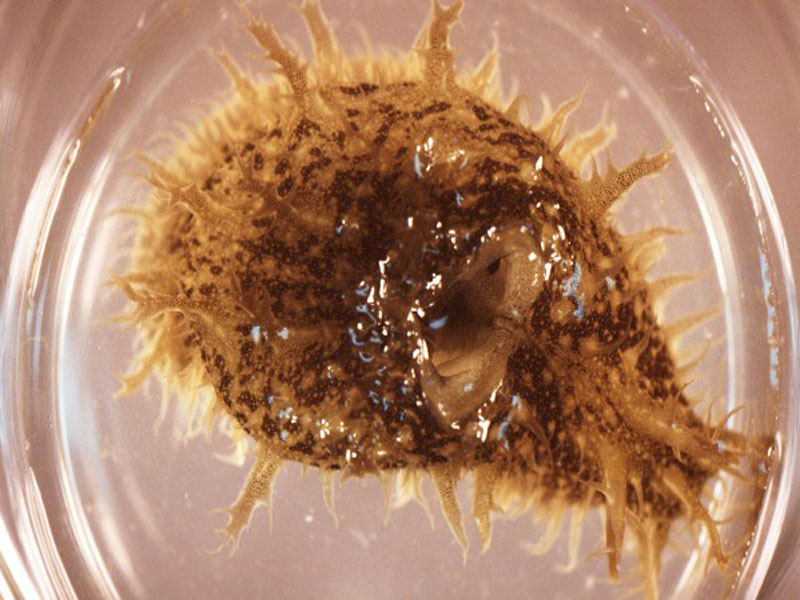
Pigmy Sea Cucumber, Five-Lined Sea Cumber, Red Footed Sea Cucumber
Description
The pygmy sea cucumber is often seen adhering to substrate in shallow rocky bottoms or seagrass beds, usually in high salinity and clear waters. Its long body, which is stiffer than most other sea cucumbers, appears chocolate-brown in color with four rows of yellow or pink tube feet. The unusually large tube feet of this species are highly modified and are adapted for clinging. Ten feathery, black, tentacles located on the anterior end are used for feeding. The pygmy sea cucumber can reach a length of 4 inches.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This sea cucumber is a detritivore, meaning that it feeds on organic wastes. In doing so, it can consume clam feces and pseudofeces, removing these wastes from the clam bag.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
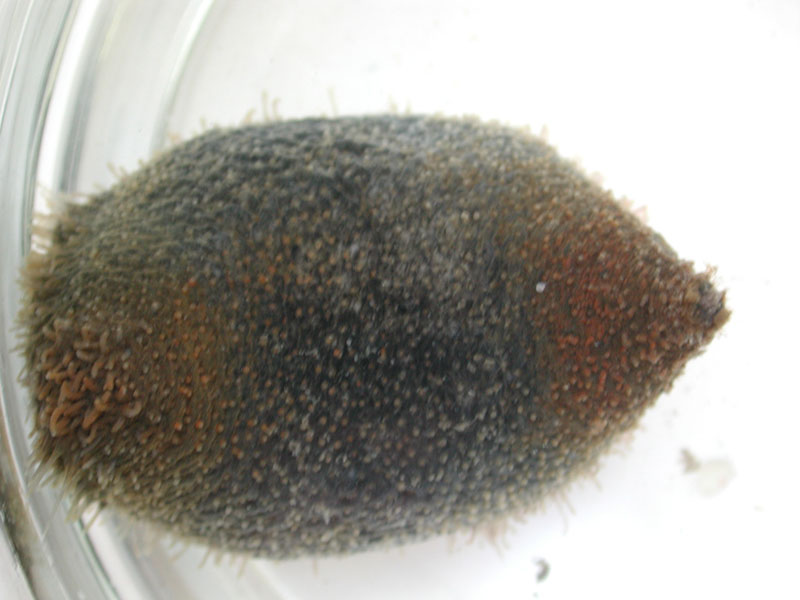
Brown Sea Cucumber
Description
The brown sea cucumber is found on mud or sand bottoms from the low-tide line to water 20 feet deep. The hairy, pear-shaped body can be blackish, brownish, greenish, or purplish in color and is covered with slender, translucent, randomly distributed tube feet. Its soft body is wide in the middle and tapers towards the ends, with both ends oriented upwards. The animal burrows in the sediments with tentacles and anus projecting above the surface. Ten large, bushy tentacles located on the anterior end are used for feeding. This sea cucumber can grow up to 6 inches long and 2 inches wide.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This sea cucumber is a detritivore, meaning that it feeds on organic wastes. In doing so, it can consume clam feces and pseudofeces, removing these wastes from the clam bag.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.

Taxonomy
- Kingdom:Animalia
- Phylum: ECHINODERMATA
- SubPhylum: Echinozoa
- Class: Holothuroidea
- Order: Dendrochirotida
- Family: Sclerodactylidae
- Genus: Sclerodactyla
- Species: briareus
White Baby Ear
Description
The white baby’s ear (locally known as "snot dog") is commonly found on sandy bottoms below the low-tide line in shallow waters. This snail has a white, wide, flattened shell with a thin, yellowish periostracum (the outer layer of the shell), and reaches a length of 2 inches and a width of 1 ¼ inches. Its white mantle (tissue that lines and secrets the mollusk shell) covers the entire shell when extended, secreting large amounts of mucus when handled.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The baby’s ear is a predator of clams and can be found in clam lease areas. This snail burrows like the moon snail and also has similar predatory activities, with the only exception being that the drill hole may not be as beveled as the moon snail.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
The clam bag and cover netting are effective control methods.
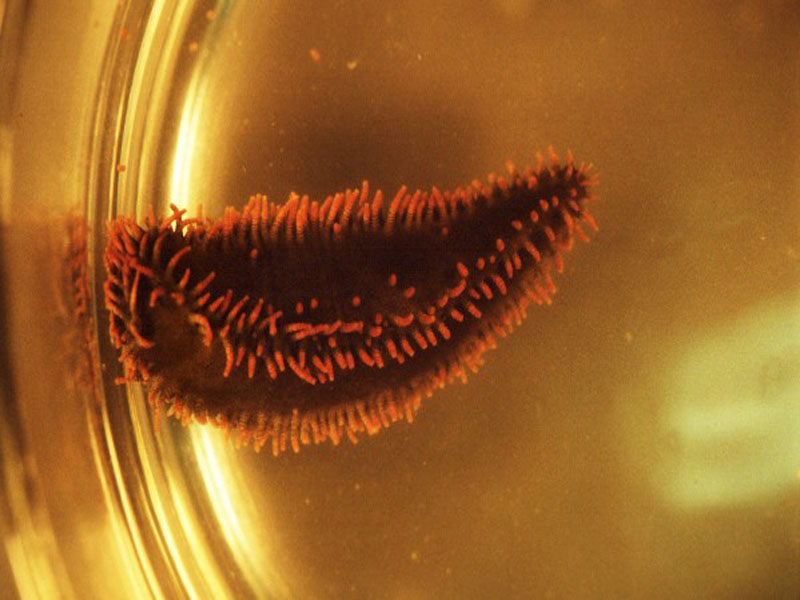
Green Sea Cucumber
Description
The green sea cucumber lives in mud flats and sea grasses and is usually found in less than 20 feet of water. Its elongate body can appear brown, mottled brown, greenish-brown, or completely black. Its thick skin is covered with bumpy calcareous spicules (small structures which support tissues of some soft-bodied invertebrates). Tube feet are arranged in double rows along its body with more rows on the bottom side. Tips of the tube feet may be red due to the presence of hemoglobin. The animal lives in a U-shape burrow with tentacles and anus projecting above ground. Their paired round holes can be seen in the bottom sediments spaced from one to three inches apart. Ten dark-brown tentacles are laid on the sediment or swept through the water to pick up detritus, which is sucked from the tentacles when placed in the mouth. This sea cucumber can grow up to 6 inches in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This sea cucumber is a detritivore, meaning that it feeds on organic wastes. In doing so, it can consume clam feces and pseudofeces, removing these wastes from the clam bag.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
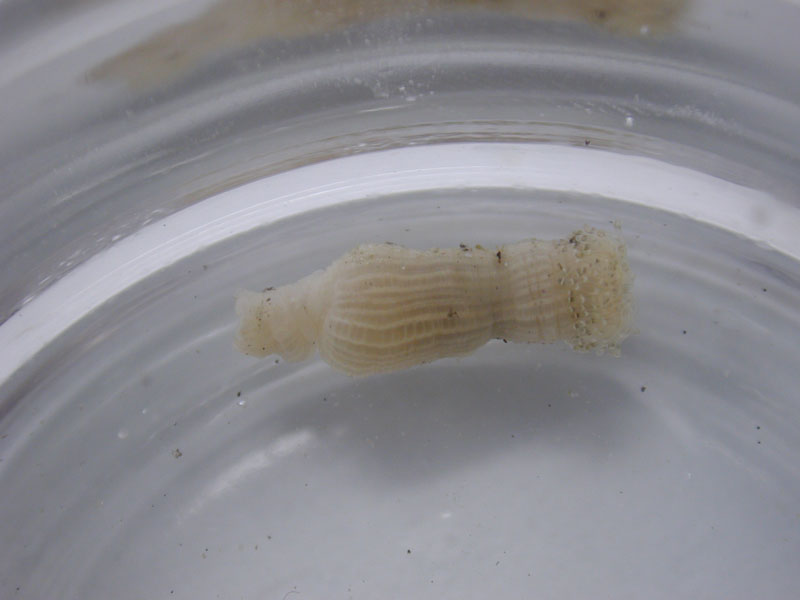
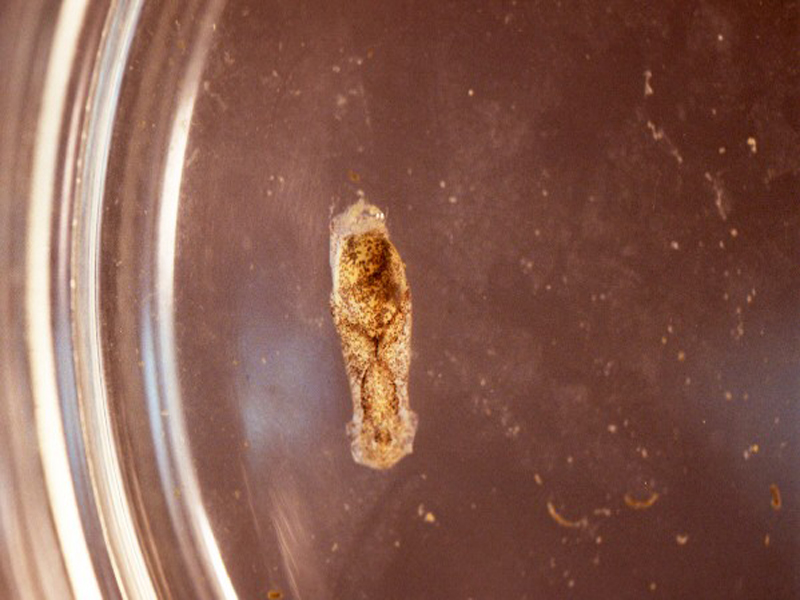
Striate Bubble
Description
The striate bubble is a common gastropod (snail) of shallow, grassy mud flats from North Carolina to the West Indies. It has a dome-like shell with a broad aperture and reaches almost 1 inch in length. The shell is white with irregular brown striations, and when the body of the animal is extended, it completely envelops the shell. The bubble snail is a hermaphrodite, meaning that both sexes are contained in one animal, and lays jelly-like ribbons in which its eggs are embedded.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The bubble snail is a herbivore, meaning that it feeds on plant material. It primarily consumes green macro algae which it grinds up with plates in its gizzard. In doing so, it can help keep clam bags free of macro algae that otherwise may foul the bag.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
Taxonomy
- Kingdom:Animalia
- Phylum: MOLLUSCA
- SubPhylum:
- Class: Gastropoda
- Order: Cephalaspidea
- Family: Bullidae
- Genus: Bulla
- Species: striata
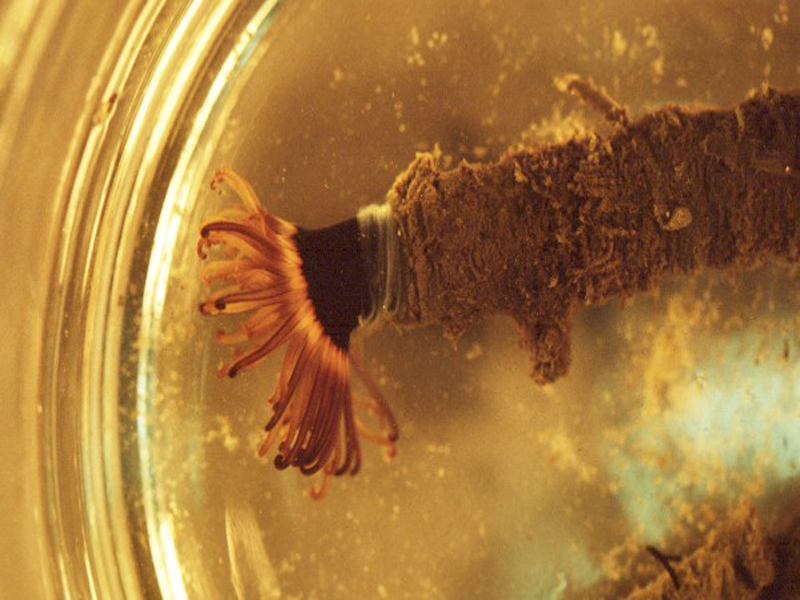
American Tube Dwelling Anemone
Description
The American tube dwelling anemone occupies muddy sand flats. This anemone inhabits a tough, silky tube that is made of tangled threads. The tube may be colonized by fouling organisms. The animal has two distinct whorls of tentacles and can withdraw into the tube. They feed by spreading the tentacles on the surface of the sand to gather food particles. Tubes may reach 20 inches in length and about 1 ½ inches in diameter.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The tube dwelling anemone coexists in the clam lease environment and clam bag, with no known effects to clams.
- NEIGHBOR
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
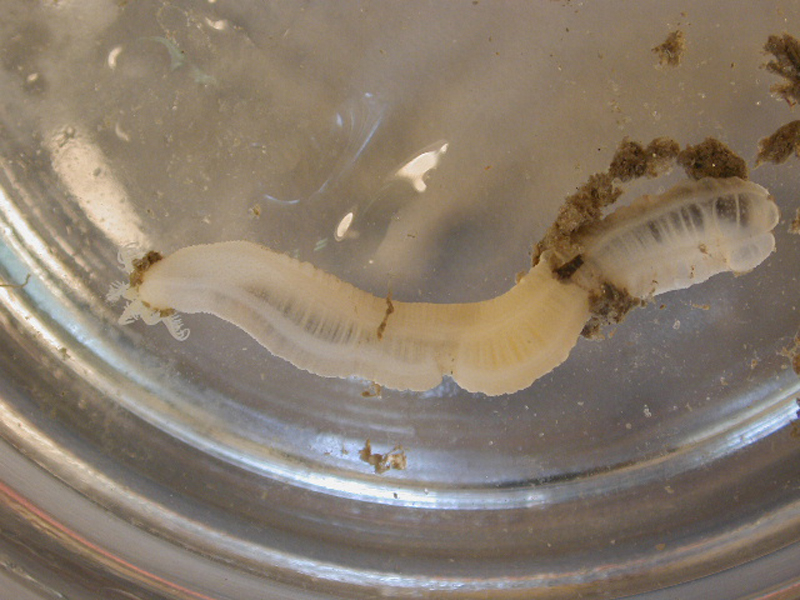
White Synapta
Description
The white synapta prefers sandy and muddy sediments in depths less than 3 feet, and sometimes is found in association with seagrasses. The body of this worm-like sea cucumber is fragile, smooth and translucent white, allowing the internal organs to show through. Five white longitudinal muscle bands are visible through the body wall. No tube feet are present; rather a series of calcareous plates are used for attachment. Twelve retractable, feather-like tentacles, each with 5-7 branches on the opposite sides of the stalk, surround the mouth. The body is buried under the mud while its tentacles extend on the surface to pick up detritus. Its burrow is surrounded by small mounds of fine sand with a central opening ¼ inch wide. The white synapta reaches 6 inches in length and 3/8 inches in width.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The white synapta is a detritivore, meaning that it feeds on organic wastes. In doing so, it can consume clam feces and pseudofeces, removing these wastes from the clam bag.
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.