Crab-like
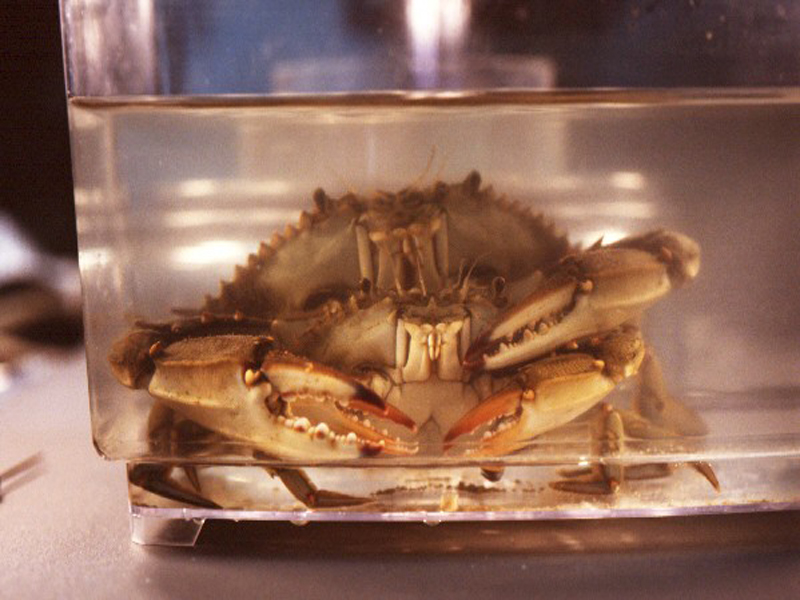
Blue Crab
Description
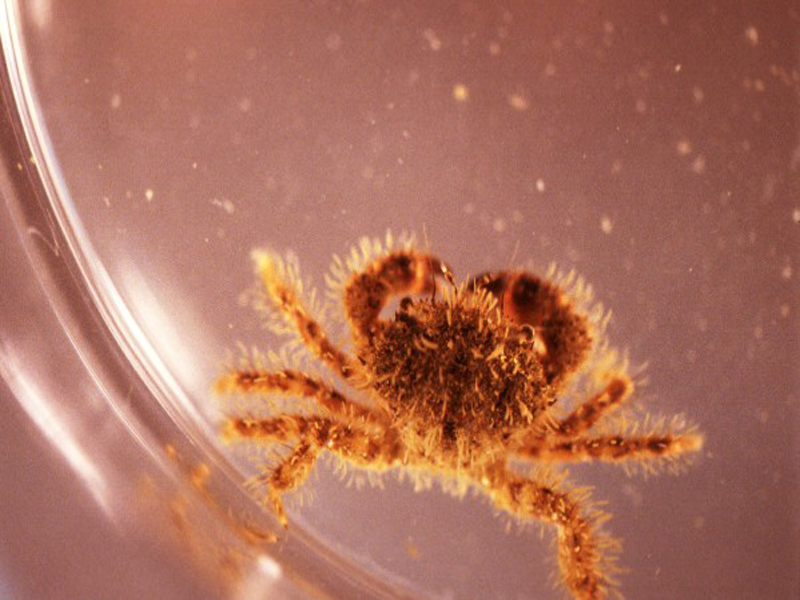
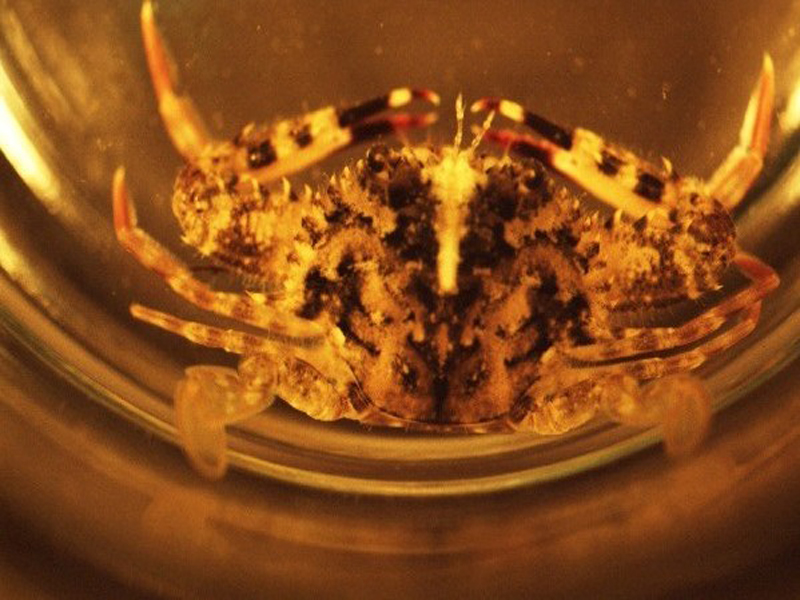
The blue crab is the largest and most important, economically, of the swimming crabs. Found widespread among Southeastern, Atlantic, and Gulf of Mexico coasts, the blue crab supports large commercial fisheries. These crabs are characterized by wide carapaces with sharp spines on either side, and the last pair of legs has been modified into swimming paddles. Their carapace can reach 9 inches in width and 4 inches in length, and is a blue-grey color, with granulations on the top. There are eight teeth on either side of the carapace between the spine and the eyes, and there are two teeth between the eyes on the carapace. Females are differentiated from males by having red tips on their claws. Blue crabs will feed on anything ranging from other crabs and shrimp to decaying flesh, and are some of the more aggressive of the crabs, raising their claws in defense when approached.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Blue crabs prey heavily on almost all sizes of clams. Blue crabs are voracious consumers of hard clam seed with rates of clam consumption greater than those reported for any other bivalve species (Krauter and Castagna, eds., 2001). Clam size is the most important factor in the rate of crab predation. Only very large blue crabs can consume clams greater than pasta-size (about 30-35 mm shell length). Considered a scavenger, the blue crab typically opens a clam with their claws by crushing the entire clam, chipping a valve (shell) edge, or forcing the valves apart. Evidence of blue crab predation includes chipped edges or crushed shells, as well as torn or ripped clam bags.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Predator control for blue crabs includes the clam bag and, if needed, additional protective covering, such as chicken wire or plastic netting. Blue crabs can be removed from the aquaculture lease area by using crab traps. Clam farmers can apply for a depredation endorsement with their Saltwater Products License that allows them to possess up to 75 blue crab traps for the incidental take of destructive or nuisance crabs within 1 mile of their aquaculture lease. Sale of blue crabs taken with a depredation endorsement is prohibited. Visit the website of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission <HYPERLINK TO www.floridaconservation.org> for more information. Caution should be taken when handling blue crabs as their pincher claws are powerful and can inflict a serious cut.
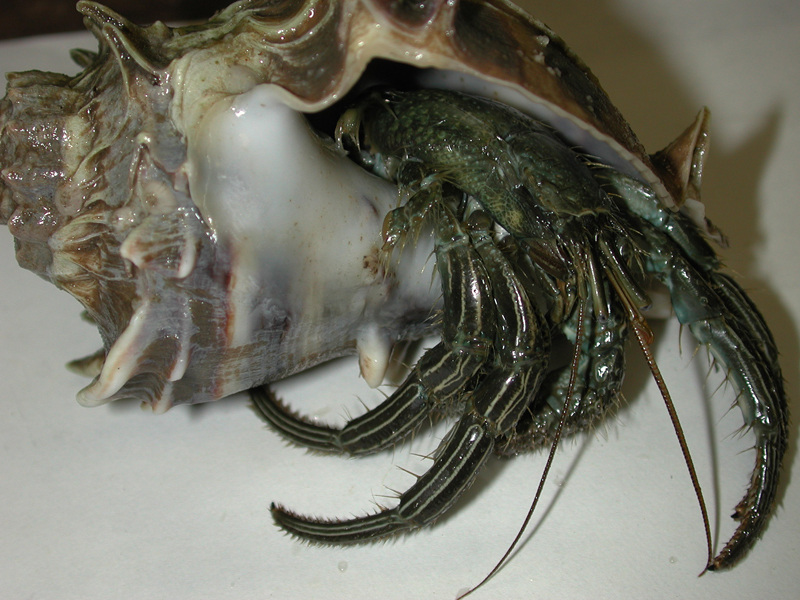
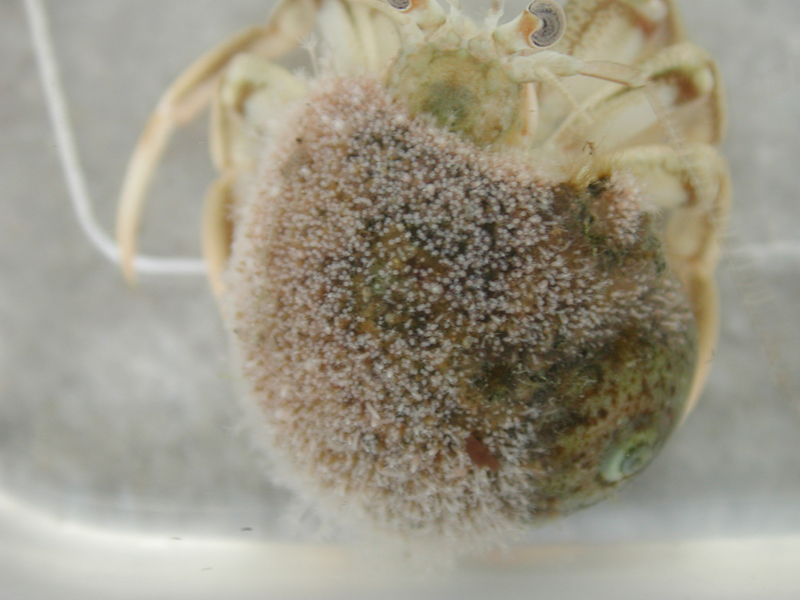
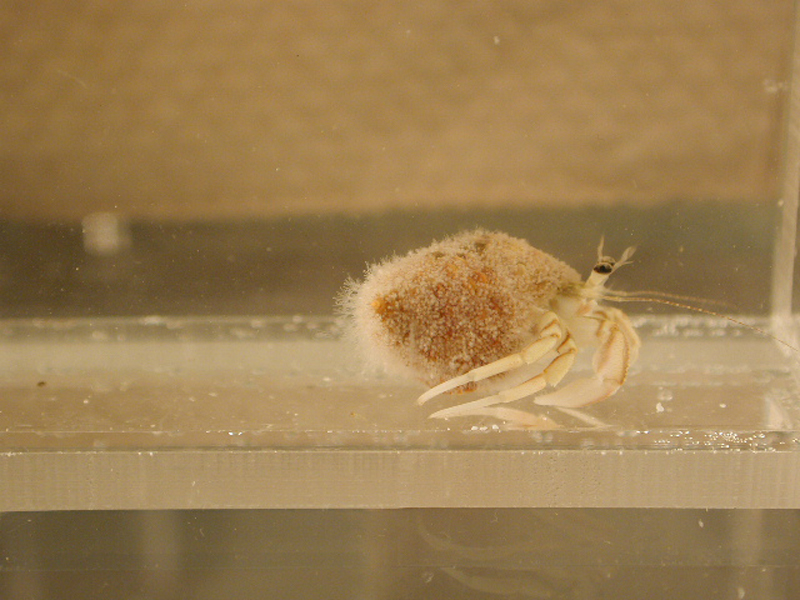
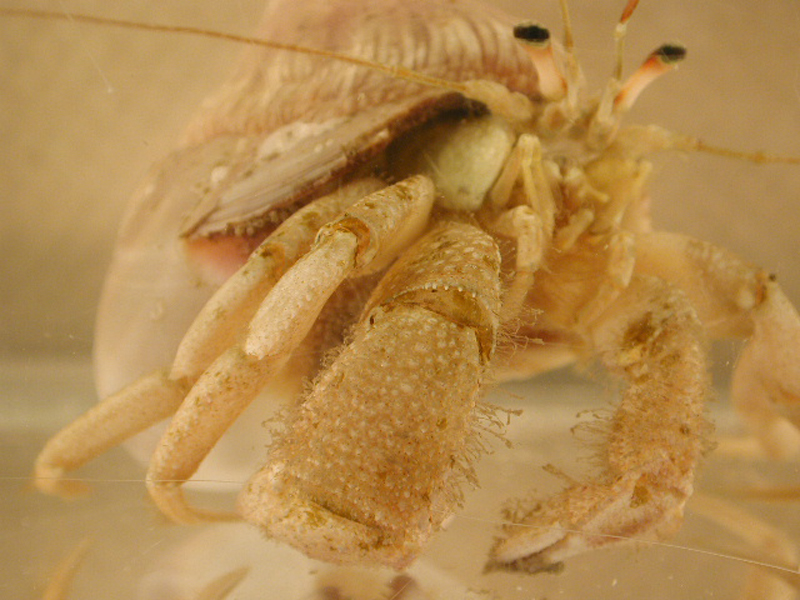
Thinstripe Hermit Crab
Description
The thinstripe hermit crab is one of the largest of the common hermit crabs found from Virginia to Caribbean shores. It is often found on mud flats or rock jetties in a variety of snail shells, and can reach a length of 3 inches. It is very distinct in that the walking legs are lined with four white stripes down the length of each leg. The crab is otherwise a greenish to dark brown color, with orange antennae. The claws are equal sized, and its fingers are spooned. Adults can often be found in tulip snail or pear whelk shells, though they are not immune to the stings of snail fur, and thus will not be seen in shells harboring these hydroids. These crabs feed on scavenged material, detritus, or macro algae.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Thinstripe hermit crabs are herbivores and consume macro algae, in particular sea lettuce. They can assist in reducing fouling organisms found on the bag
- FRIEND
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
No action needs to be taken by a clam farmer.
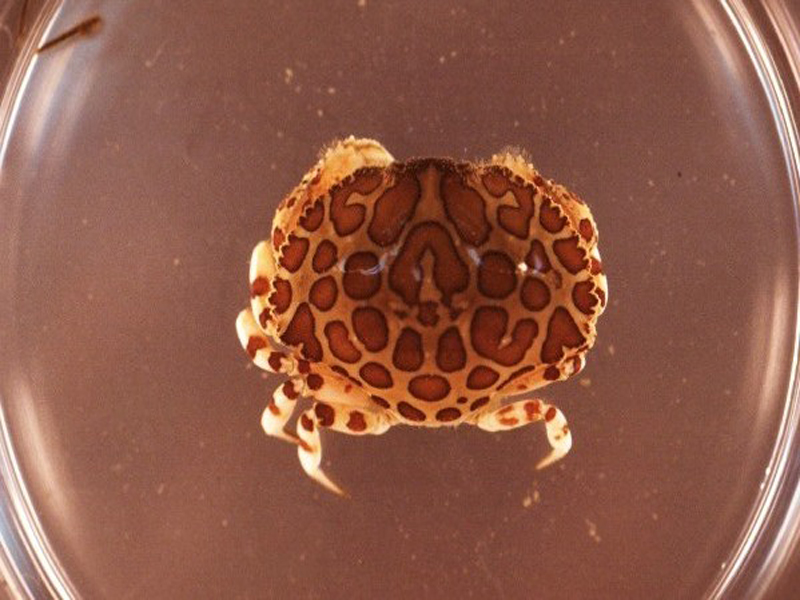
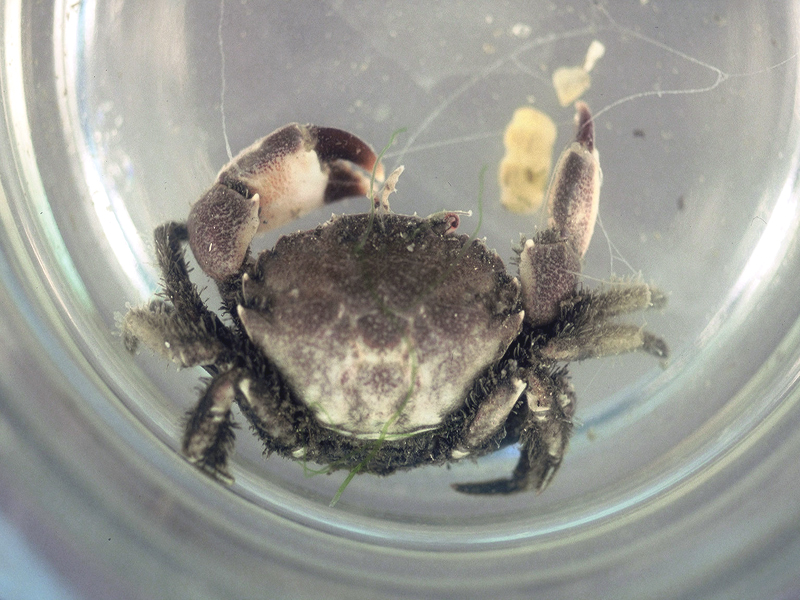
Say's Mud Crab
Description
The Say's mud crab is a smaller, yet still common, mud crab of the Atlantic and Gulf coasts. Reaching just over 1 inch long, this mud crab is found along mud and oyster shell bottoms, but can also be found among seagrasses. The claws are of unequal size, and the fingers are dark brown or black, bearing a slight curve at the tips. The claws do not have large teeth at the base of the fingers as do many other mud crabs. The front sides of the shell have 4 teeth, though the front-most tooth is obscured just behind the eyes, and there is a distinct indentation in the middle of the carapace between the eyes. They feed on acorn barnacles, juvenile clams of the genus Mercenaria, and other invertebrates in their environment.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Mud crabs are predators of cultured clams and the most common crab species found in the clam lease environment. These crabs attack clams by patiently chipping away at the shell margin with a large tooth-like structure on their larger claw. Predatory activity is limited by clam size. Mud crabs select smaller clam seed with only the very large mud crabs capable of consuming clams up to 20 mm in shell length (Krauter and Castagna, eds., 2001). On the other ‘claw’, mud crabs also eat very small fouling organisms. In doing so, they assist in keeping the surface of a clam bag clean.
- FRIEND, FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Predator control for mud crabs includes the clam bag and if needed, additional predator covering, such as chicken wire or plastic netting. Dipping of nursery bags with a net coating, which stiffens the mesh, may also minimize predation of clam seed by mud crabs.

Taxonomy
- Kingdom:Animalia
- Phylum: ARTHROPODA
- SubPhylum: Crustacea
- Class: Malacostraca
- Order: Decapoda
- Family: Panopeidae
- Genus: Dyspanopeus
- Species: sayi
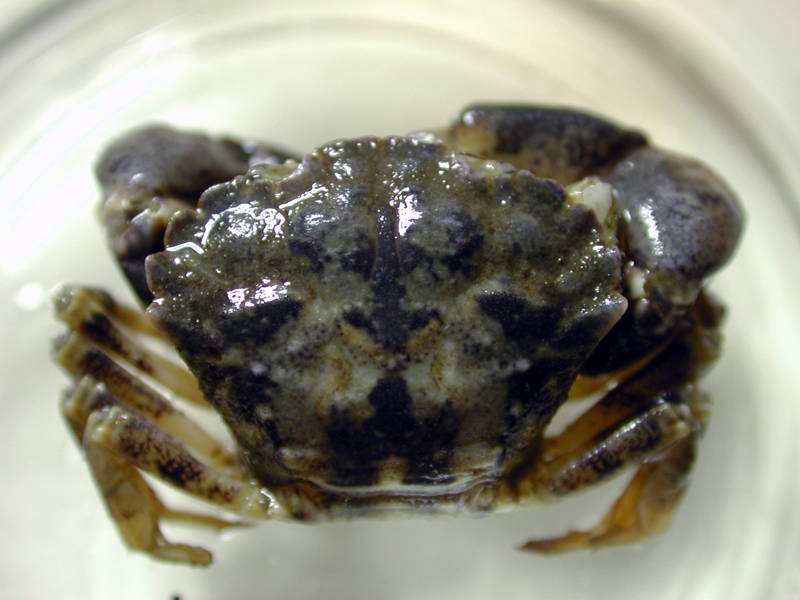
Flatback Mud Crab
Description
The flatback mud crab is found on mud bottoms in bays and brackish estuaries often occurring with oysters. It preys on newly settled oysters, but is not considered a serious pest by oystermen. The fan-shaped crab is grayish-olive to olive-brown, lighter underneath, the fingers of the pincers dark brown. The carapace is rounded in front, with the sides slanting in toward the rear border. Pincers appear stout and unequal, the larger pincer with the fingers almost straight, the tips of which appear hollowed out or "spoon-shaped". This small mud crab is ½ inch long and ¾ inch wide.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Mud crabs are predators of cultured clams and the most common crab species found in the clam lease environment. These crabs attack clams by patiently chipping away at the shell margin with a large tooth-like structure on their larger claw. Predatory activity is limited by clam size. Mud crabs select smaller clam seed with only the very large mud crabs capable of consuming clams up to 20 mm in shell length (Krauter and Castagna, eds., 2001). On the other ‘claw’, mud crabs also eat very small fouling organisms. In doing so, they assist in keeping the surface of a clam bag clean.
- FRIEND, FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Predator control for mud crabs includes the clam bag and if needed, additional predator covering, such as chicken wire or plastic netting. Dipping of nursery bags with a net coating, which stiffens the mesh, may also minimize predation of clam seed by mud crabs.
Calico Box Crab, Rooster Crab, Shame-Faced Crab
Description
The calico box crab occupies sand bottoms in bays and the open ocean from below the low-tide line to water 150 feet deep. This crab is very active, has a greater gill area, and hence greater capacity to take in oxygen than most crabs. It is fan-shaped with a broadly rounded carapace, which is yellowish, grayish, or brownish in color with many large, round or irregular, light red spots and dark borders. The pincers are strong and equal and with a row of coarse, low, round projections on the outer surface of the hand. The calico box crab can obtain a carapace width of 2 ½ inches and a length of 1 ¾ inches.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Calico crabs could be a potential predator on clams, but are infrequently observed on clam aquaculture leases.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Clam bags and cover netting should be adequate protection against potential rooster crab predation.
Smooth Mud Crab
Description
The smooth mud crab occurs commonly on both shelly and soft sandy bottoms. This small crab is dark reddish brown to dark gray in color, often with a light yellow band along the front edge of the carapace. The pincers are unequal with the upper finger of the larger pincer having a large tooth at the base. The smooth mud crab can reach a length of almost 1 inch.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Mud crabs are predators of cultured clams and the most common crab species found in the clam lease environment. These crabs attack clams by patiently chipping away at the shell margin with a large tooth-like structure on their larger claw. Predatory activity is limited by clam size. Mud crabs select smaller clam seed with only the very large mud crabs capable of consuming clams up to 20 mm in shell length (Krauter and Castagna, eds., 2001). On the other ‘claw’, mud crabs also eat very small fouling organisms. In doing so, they assist in keeping the surface of a clam bag clean.
- FRIEND, FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Predator control for mud crabs includes the clam bag and if needed, additional predator covering, such as chicken wire or plastic netting. Dipping of nursery bags with a net coating, which stiffens the mesh, may also minimize predation of clam seed by mud crabs.
Snail Fur
Description
Snail fur is a pink to white mat-like growth on the gastropod (snail) shells occupied by hermit crabs. Within the mat, there are three types of polyps: 1) a club-like feeding polyp that grows up to ½ inch in length, with upper and lower circles of eight tentacles, the lower set being shorter than the upper; 2) male and female reproductive polyps that have a few short terminal tentacles; and, 3) specialized defensive stinging polyps that are long coils and look thread-like. This is an example of mutualism – the hermit crab receives protection from the hydroid's nematocysts (stinging cells), while the hermit crab carries the hydroid to plankton-inhabited areas.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Snail fur is only found attached to the shell of hermit crabs. They are filter feeders and can compete for the same food source (micro algae) as clams.
- FOE
- Competitor
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Snail fur is infrequently found in clam bags and rarely poses a problem.
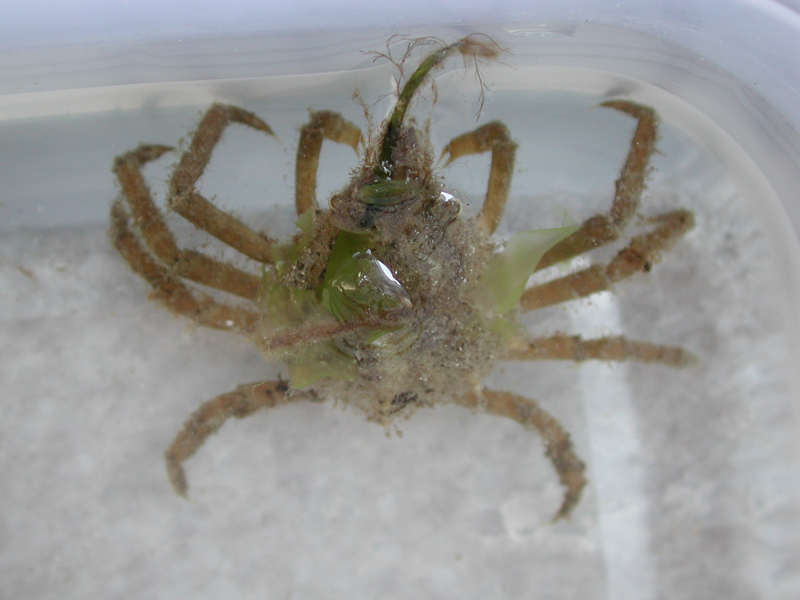
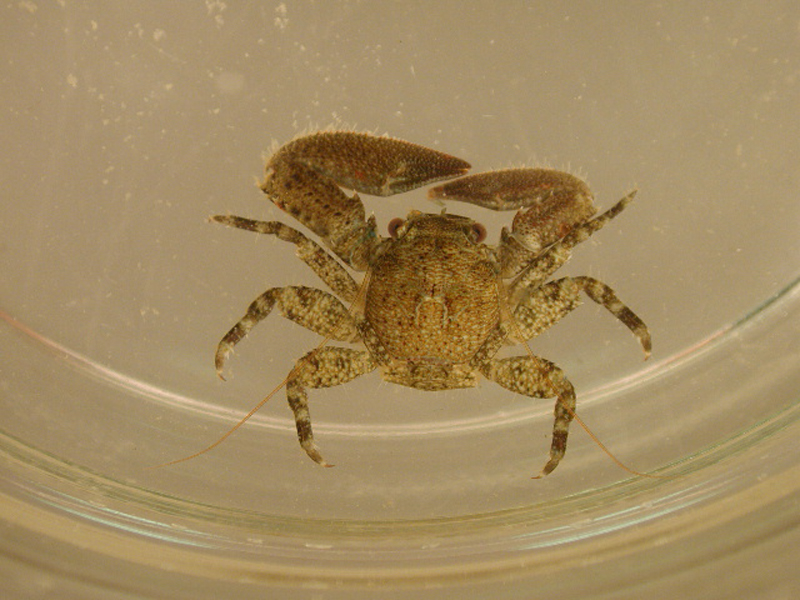
Longnose Spider Crab
Description
The longnose spider crab is a sluggish crab commonly found in the southeastern U.S. on most bottom substrates, though preferring quiet waters. It has a rounded carapace, and a forked rostrum projecting from between the eyes. Adults have 6 prominent spines along the length of the back, but the brown carapace is otherwise covered in small spines. Immature individuals can often be found overgrown with algae, sponges, hydroids and tunicates on the shell, while adults are usually clear of fouling. Juveniles have been known to ride on cannonball jellyfish and moon jellyfish, apparently feeding upon the cnidarians. It can reach almost 4 inches in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
There does not appear to be any reports linking spider crabs to predation on hard clams, but it is possible these crabs could prey on small clam seed. On the other ‘claw’, spider crabs typically eat very small fouling organisms. In doing so, they assist in keeping the surface of a clam bag clean.
- FRIEND, FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
As with other crabs, predator control includes the clam bag and, if needed, additional protective covering, such as chicken wire or plastic netting.
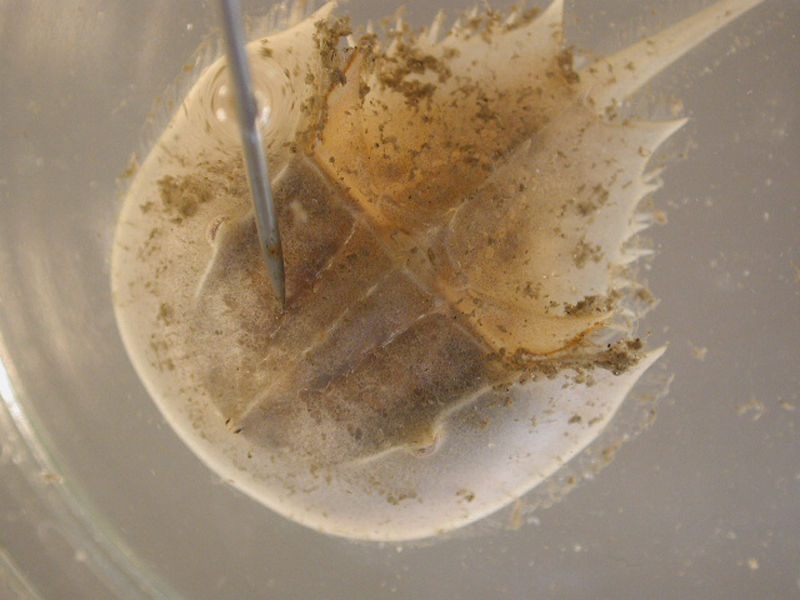
Horseshoe Crab
Description
The horseshoe crab is common on mud or sand bottoms from near low-tide line to water 75 feet deep. This animal is the only one of its kind in American waters, and cannot be confused with anything else. It feeds on small clams, worms, and other invertebrates which it grinds with the burr-like bases of the walking legs that surround its mouth. This large crab has a greenish-tan, horseshoe-shaped carapace with triangular abdomen and spike-like tail. A pair of compound eyes is located on each side of the carapace and two simple eyes are present on the forepart of the midline. The sides of the abdomen are scalloped with six spines. The mouth is surrounded by 5 pairs of walking legs; the first pair on males is rounded and heavy, while the others have pincher tips. The underside of the abdomen has six pairs of overlapping flaps, the first covering an opening of six ducts, the others covering five pairs of book gills comprised of many flat sheets. The horseshoe crab can obtain a length of 2 feet and a width of 1 foot. Males are about one-third the size of females.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Horseshoe crabs are capable of eating very small clam seed. Large adult horseshoe crabs may uncover clam bags as they search and feed on worms found on the lease bottom. Their feeding behavior could expose clam bags to other predators.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Typically the nursery clam bag provides adequate protection from horseshoe crab predation. Adequate cover netting should minimize the risk of exposed clam bags becoming vulnerable to other predators.
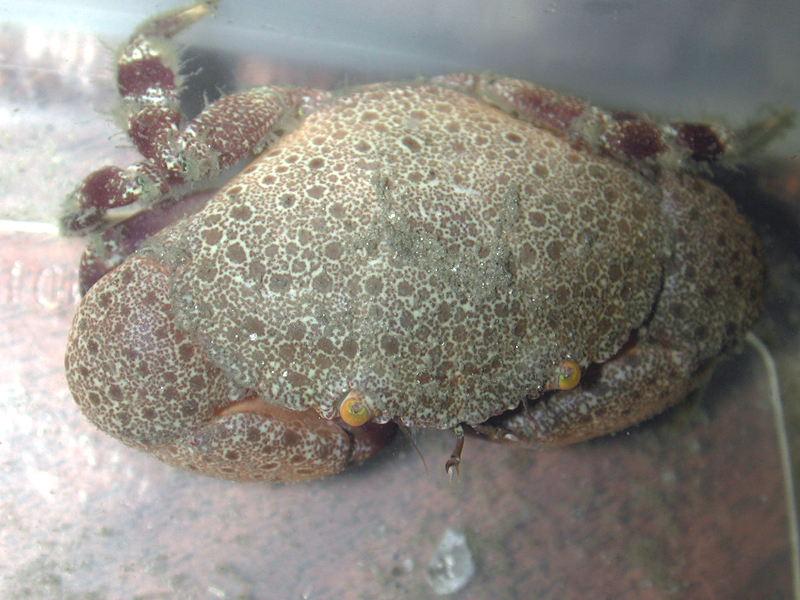
Florida Stone Crab
Description
The Florida stone crab is another commercially important species of crab. They range from North Carolina to the West Indies, and can reach a length of 5 inches across the carapace. One of the largest members of the mud crab family, stone crabs have large, thick claws and a smooth, heavy carapace. The colors of the crab change from glossy purple to speckled grey to tan as they mature, yet always maintain dark colored fingers. The front sides of the carapace have four flattened teeth, and the claws are of unequal sizes, one as crushers and one for pincers. Adults burrow in the mud flats underneath rocks, corals, and oysters. They feed upon acorn barnacles, oysters and a variety of other invertebrates.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The stone crab is capable of consuming large clams and is a serious predator in certain growing areas. Evidence of stone crab predation includes crushed shells, usually larger shell fragments than found with blue crab predation, as well as torn or ripped clam bags.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Predator control for stone crabs includes the clam bag and, if needed, additional protective covering, such as chicken wire or plastic netting. Stone crabs can be removed from the aquaculture lease area by using crab traps. Clam farmers can apply for a depredation endorsement with their Saltwater Products License that allows them to possess up to 75 stone crab traps for the incidental take of destructive or nuisance crabs within 1 mile of their aquaculture lease. Sale of stone crabs taken with a depredation endorsement is prohibited. Visit the website of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission <HYPERLINK TO www.floridaconservation.org> for more information. While they appear much more sluggish than blue crabs, and are readily handled, it should still be noted that their claws can easily crush a finger.
Longwrist Hermit Crab
Description
The long wrist hermit crab is one of the most common decapod (10-legged) crabs found along the soft-bottomed shallows from Massachusetts to the Gulf of Mexico. It reaches about 1 inch in length, and is found in a variety of empty snail shells. The right claw is much longer than the left claw, being nearly cylindrical, smooth and hairless. The fingers of the left claw are spooned, and the right claw has a long stripe on each side. Walking legs are iridescent, and the carapace is a light green color. They have been found to subsist on a diet of diatoms (micro algae), detritus and macro algae, along with scavenged material.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
These hermit crabs are opportunistic feeders, meaning they consume any available organic material. They may consume unburied stressed clams, but not buried healthy clams.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Clams in buried bottom bags are protected from possible hermit crab predation.
Flatclaw Hermit Crab
Description
The flatclaw hermit crab is a larger species of hermit crab, reaching up to 1 ¼ inches in length, and ranges from Massachusetts to the Gulf of Mexico, living in intertidal zones similar to the long wrist hermit crab. As the name implies, both claws are large and flat, with the right claw larger than the left. The large claw has serrations around the edge, and is usually a white or cream color. They feed upon detritus, macro algae and scavenged material, and when disturbed will retreat into their shell using the large flat claw as a door. Larger individuals are often found in moon snail and lightning whelk shells, and they sometimes adorn their shells with the tricolor anemone, which serves as a protective symbiont (two species that have long-term interdependence between them).
What Are The Effects On Clams?
These hermit crabs are opportunistic feeders, meaning they consume any available organic material. They may consume unburied stressed clams, but not buried healthy clams.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Clams in buried bottom bags are protected from possible hermit crab predation.
Atlantic Mud Crab
Description
Behind the stone crab, the common mud crab is the largest of the mud crabs, reaching 2.5 inches in length. Common along mud flats, oyster reefs, and mangrove roots from Massachusetts to South America, this mud crab has 5 spines along the front sides of the carapace, and an indentation between the eyes. Claws are large and heavy, the right one being larger than the left. The fingers are often a black color, and the dark color of the bottom finger usually extends a little onto the palm. The larger claw also has a distinct, white tooth at the base of the top, moveable finger. These mud crabs are known to feed on oysters as well as acorn barnacles, juvenile clams of the genus Mercenaria, and other invertebrates in their environment.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Mud crabs are predators of cultured clams and the most common crab species found in the clam lease environment. These crabs attack clams by patiently chipping away at the shell margin with a large tooth-like structure on their larger claw. Predatory activity is limited by clam size. Mud crabs select smaller clam seed with only the very large mud crabs capable of consuming clams up to 20 mm in shell length (Krauter and Castagna, eds., 2001). On the other ‘claw’, mud crabs also eat very small fouling organisms. In doing so, they assist in keeping the surface of a clam bag clean.
- FRIEND, FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Predator control for mud crabs includes the clam bag and if needed, additional predator covering, such as chicken wire or plastic netting. Dipping of nursery bags with a net coating, which stiffens the mesh, may also minimize predation of clam seed by mud crabs.
Green Porcelain Crab
Description
The green porcelain crab is a small crab, distributed throughout the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean shores, found often along rocky rubble, oyster bars and other intertidal hard substrates. It reaches a maximum size of about 1 inch in carapace width. Both claws are of equal size and, despite their relatively large size, do not offer a hard pinch. The green porcelain crab is often brownish to green in coloration, and has bead-like projections all over the carapace and claws. On each claw, there are three spines on the inside edge of the wrists that help differentiate it from another common porcelain crab.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Green crabs are filter feeders and can consume similar phytoplankton (micro algae) species as hard clams.
- FOE
- Competitor
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Green porcelain crabs are infrequently found in clam bags and rarely pose a problem.
Spineback Hairy Crab
Description
The spineback hairy crab is found in a variety of habitats, including shelly bottoms, pilings, wrecks, reefs, rocks, and mangrove swamps. This small oval crab appears grayish to reddish-brown. All but the rear third of its carapace is covered with yellow hairs, including the surfaces of its walking legs. Its robust, unequal claws are black-fingered and also covered with hairs and sharp black spines, which often occur in rows. The spineback hairy crab can reach a carapace length of 1 inch and a width of 1½ inches.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This crab can attack clams by patiently chipping away at the shell margin with a large tooth-like structure on its larger claw. However, predatory activity is limited by clam size with smaller clam seed generally selected. On the other ‘claw,’ this crab also eats very small fouling organisms. In doing so, it assists in keeping the surface of a clam bag clean.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Predator control for crabs includes the clam bag and if needed, additional predator covering, such as chicken wire or plastic netting. Dipping of nursery bags with a net coating, which stiffens the mesh, may also minimize predation of clam seed by this crab.
Iridescent Swimming Crab
Description
The iridescent swimming crab is common in shallow shelf waters and lower reaches of bays and inshore waters, mostly found on sandy or muddy bottoms. This swimming crab has a brownish-red to tan carapace with small, iridescent patches on the edge. The front sides of the legs look iridescent purple-red in the light. Its carmine-red pincers are twice the body length, strong and sharp with the last pair of walking legs being paddle-shaped.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
These swimming crabs are often mistaken for juvenile blue crabs. Like blue crabs, swimming crabs can prey heavily on small clams. Since they do not get as large as blue crabs, they generally do not affect larger clam sizes. Considered a scavenger, the swimming crab typically opens a clam with its claws by crushing the entire clam, chipping a valve edge, or forcing the valves apart. Evidence of crab predation includes chipped edges or crushed shells, as well as torn or ripped clam bags.
- FOE
- Predator
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Predator control for swimming crabs includes the clam bag and, if needed, additional protective covering, such as chicken wire or plastic bird netting.