Plant-like
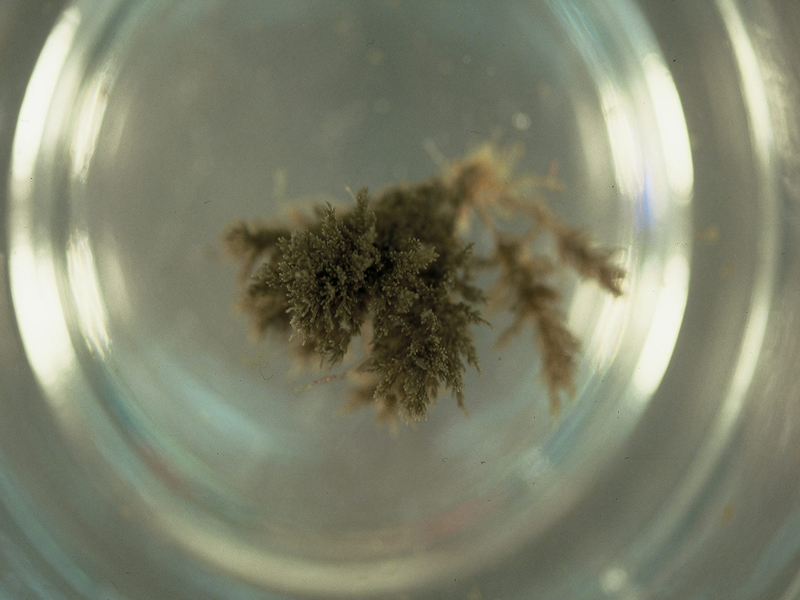
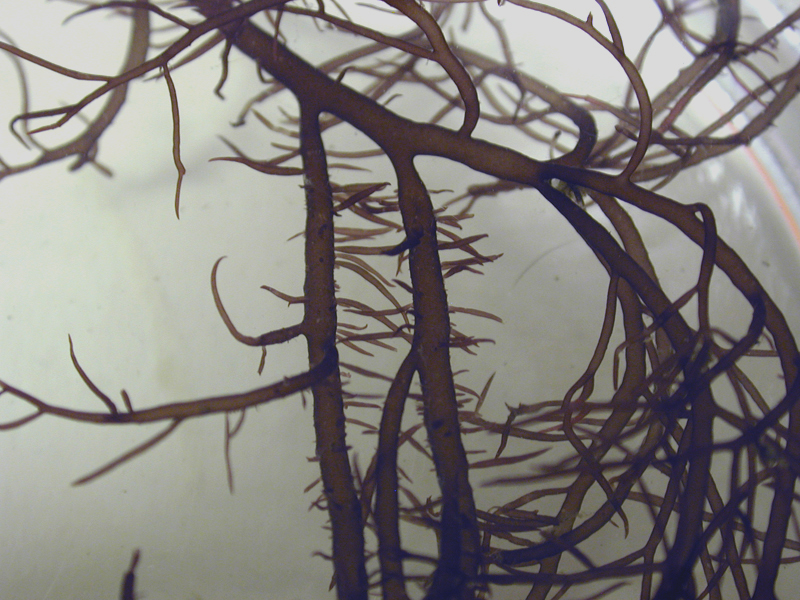
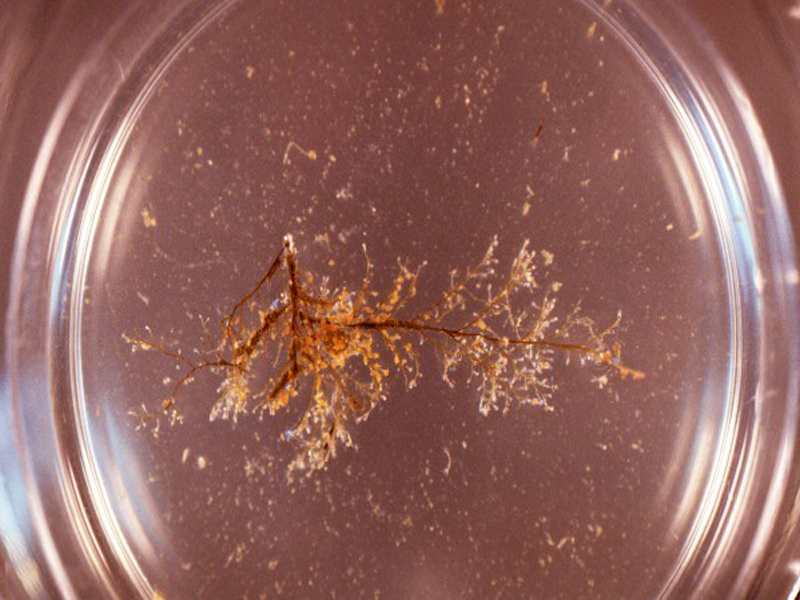
Bushy Bryozoan
Description
The bushy bryozoan is a branching bush-like bryozoan that inhabits hard substrates, primarily in the intertidal zone. Colonies are grey-brown and hang limply when the tide is out. Bushy bryozoan colonies are about 2 ½ inches in height.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The bushy bryozoan is a filter feeder and therefore competes with clams for the same types of food (micro algae). It can also be a fouling nuisance on clam bags. If fouling is extensive enough to restrict water flow into the bags, clams may suffocate, especially at high water temperatures.
- FOE
- Competitor
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Growers should inspect culture bags to determine the extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited tidal exchange. Clumps can be manually removed by hand or with a brush and will not reattach. Extensively fouled cover netting can be replaced with clean netting.
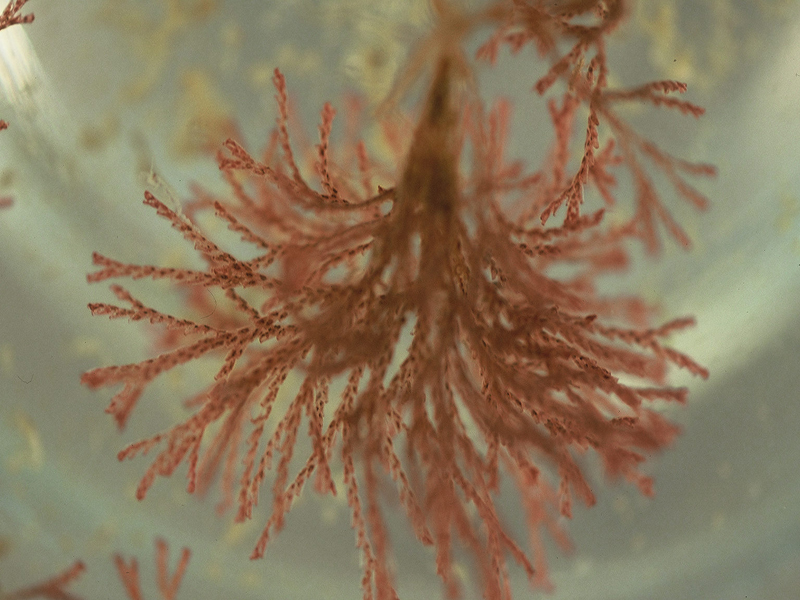
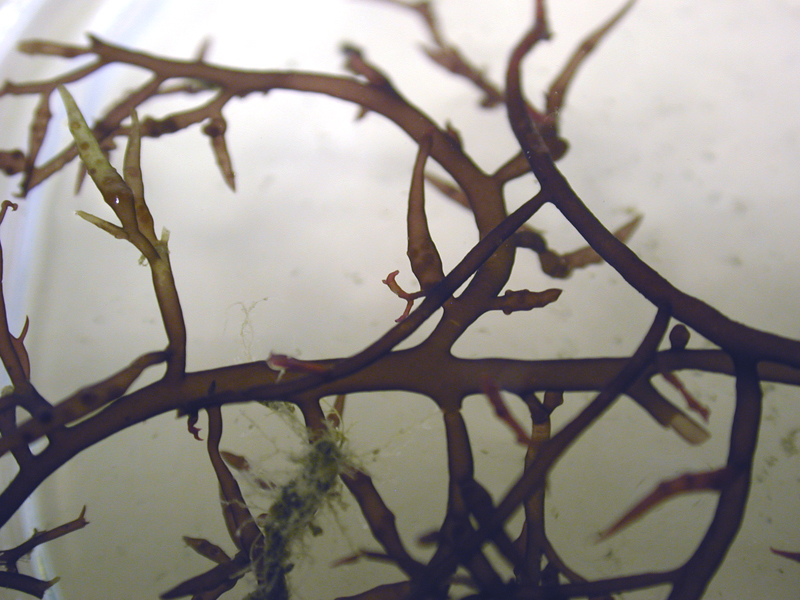
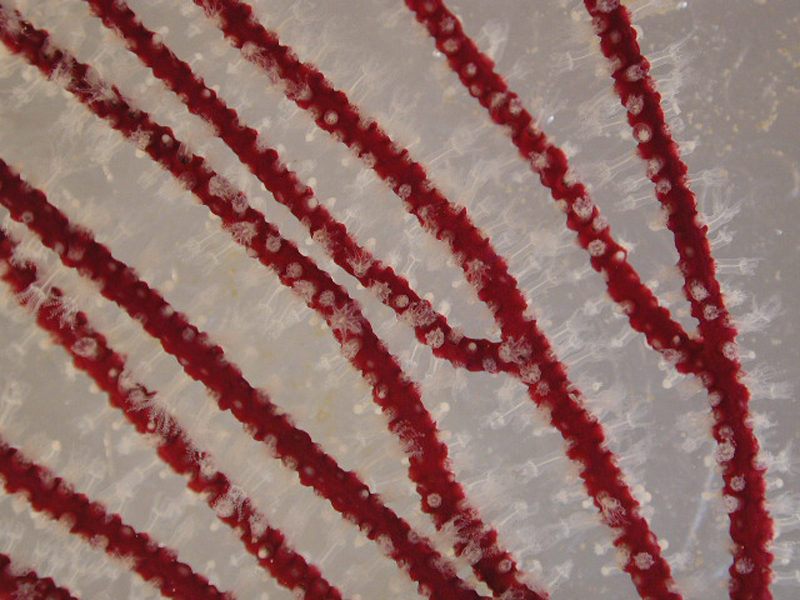
Common Bugula
Description
Bugula is a bryozoan which is commonly found worldwide. It appears as a reddish-brown, plant-like tuft up to 4 inches tall, fouling rocks, shells, pilings, debris and even crabs. Individual zooids (individuals in a colony arising through asexual reproduction) are arranged alternately in two rows along each branch, and face the same direction on the branch. They are suspension feeders, using a U-shaped lophophore (feeding organ) to catch drifting plankton. Each zooid is hermaphroditic, capable of spawning by itself.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The common bugula is a filter feeder and therefore competes with clams for the same types of food (micro algae). It can also be a fouling nuisance on clam bags. If fouling is extensive enough to restrict water flow into the bags, clams may suffocate, especially at high water temperatures.
- FOE
- Competitor
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Growers should inspect culture bags to determine the extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited tidal exchange. Clumps can be manually removed by hand or with a brush and will not reattach. Extensively fouled cover netting can be replaced with clean netting.
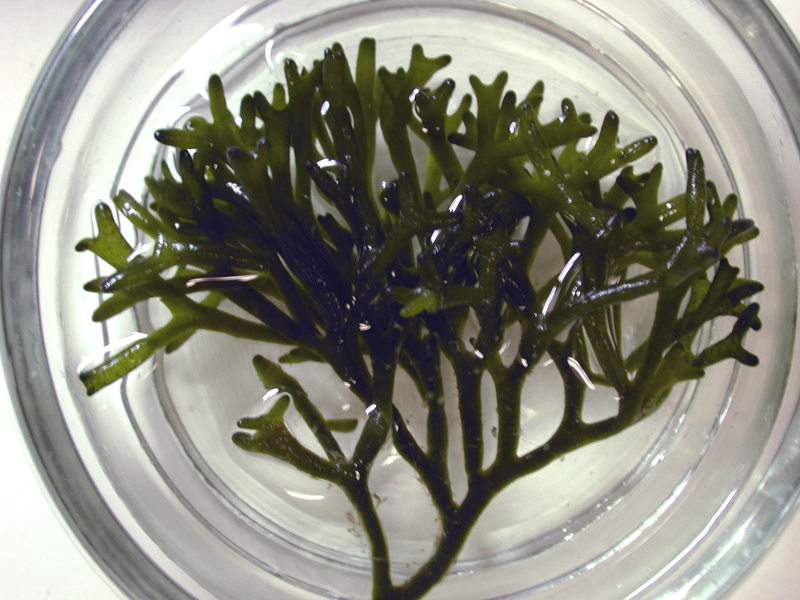
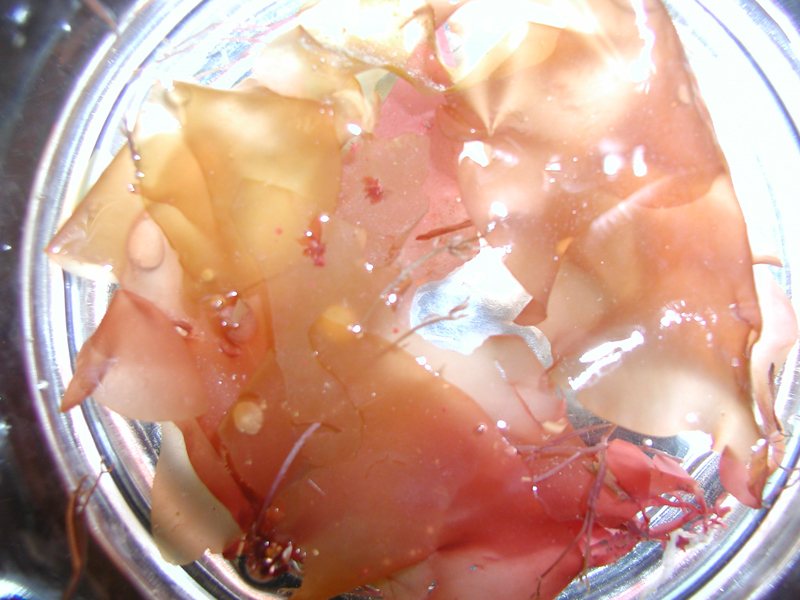
Green Fleece, Dead Man's Fingers
Description
Green fleece is a dark green macro algae that is found in intertidal and inshore subtidal zones, growing from hard bottoms. It has large, forked branches (or tubular “fingers”) with a felt-like or rubbery texture. Each branch of this macro algae is rope-like, made up of tightly interwoven microscopic filaments. The erect branches, attached from a broad disk or holdfast, can exceed 12 inches in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Green fleece has a holdfast (a root-like structure) with which it can attach to clam bags and cover netting. It can also be a drift macro algae, meaning it can float and move with prevailing currents. It can become a problem at lease areas with limited flow, such as those located in lagoons, sounds and harbors, and at high water temperatures. When it dies and decomposes on top of clam bags, it can create an anoxic (no oxygen) layer, resulting in clam mortalities.
- FOE
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Inspect bags to determine extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited flow and when water temperatures are high. If fouling over the bags is extensive, then it must be removed. Some clam growers actually use custom-designed “push” nets, operated from their boats to remove drift algae. Fouled cover netting could be removed and clean cover netting replaced over bags.
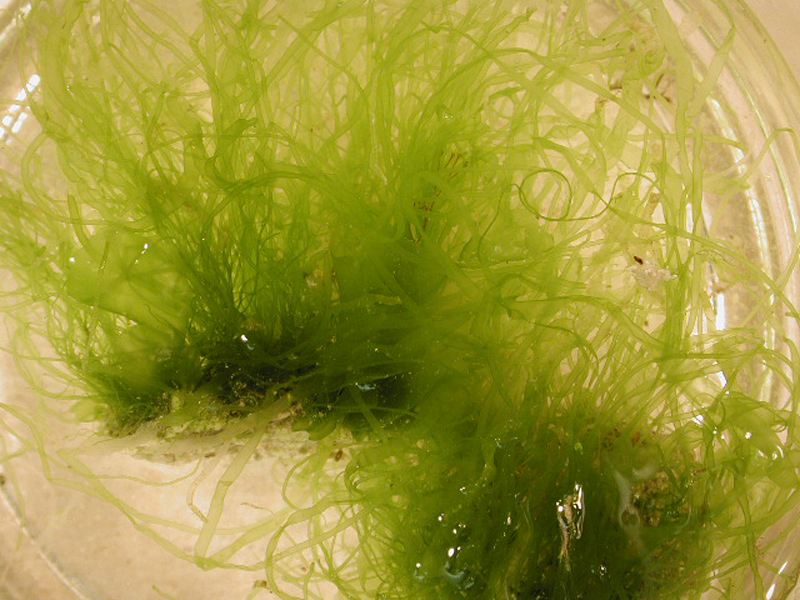
Mermaid's Hair, Angel Hair
Description
Mermaid's hair has bright green, tubular filaments and is common in quiet waters and hard bottoms. This macro algae, or seaweed, is usually found growing in dense, tangled masses and is also found mixed with other green macro algae, such as sea lettuce. It is extremely variable in length and diameter of tubes, which may by constricted at intervals. Mermaid's hair can reach a height of 12 inches tall.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Mermaid’s hair has a holdfast (a root-like structure) with which it can attach to clam bags and cover netting. It can also be a drift macro algae, meaning it can float and move with prevailing currents. It can become a problem at lease areas with limited flow, such as those located in lagoons, sounds and harbors, and at high water temperatures. When it dies and decomposes on top of clam bags, it can create an anoxic (no oxygen) layer, resulting in clam mortalities.
- FOE
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Inspect bags to determine extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited flow and when water temperatures are high. If fouling over the bags is extensive, then it must be removed. Some clam growers actually use custom-designed “push” nets, operated from their boats to remove drift algae. Fouled cover netting could be removed and clean cover netting replaced over bags.
Red Sticky Hydroid, Pink Hydroid
Description
The red sticky hydroid, or pink hydroid, has irregularly arranged, branched stems that bear polyps (attached animals with a columnar body topped by a ring of tentacles). Each trumpet-shaped polyp is surrounded by whorls of filamentous tentacles. These hydroids are often found with sea spiders, which prey on them. Colonies are colorful and reach 5 inches in diameter.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The red sticky hydroid is a filter feeder and, therefore, can compete with clams for the same types of food (micro algae). It can also be a fouling nuisance on clam bags. If fouling is extensive enough to restrict water flow into the bags, clams may suffocate, especially at high water temperatures.
- FOE
- Competitor
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Growers should inspect culture bags to determine the extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited tidal exchange. Clumps can be manually removed by hand or with a brush and will not reattach. Extensively fouled cover netting can be replaced with clean netting.
Rolling Moss, Drift Algae
Description
Found in Florida, the Bahamas, and throughout the Caribbean, this tough, wiry alga is often the principal component of mixed turfs. Found from the intertidal zone to about 20 feet deep, it will frequently attach to hard substrates only to break off and drift with the current. The branches are sparse, olive-yellow to dark red-brown, and cylindrical to slightly flatten. Branchlets, ¼ inch in size, are found scattered or arranged in opposite rows on the branches.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This macro algae can drift, meaning it floats with prevailing currents, and can be found to “roll” on the bottom. It also has a holdfast (a root-like structure) with which it can attach to clam bags and cover netting. It can become a problem at lease areas with limited flow, such as those located in lagoons, sounds and harbors, and at high water temperatures. When it dies and decomposes on top of clam bags, it can create an anoxic (no oxygen) layer, resulting in clam mortalities.
- FOE
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Inspect bags to determine extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited flow and when water temperatures are high. If fouling over the bags is extensive, then it must be removed. Some clam growers actually use custom-designed “push” nets, operated from their boats to move the algae. Fouled cover netting could be removed and clean cover netting replaced over bags.
Rolling Moss, Drift Algae
Description
This group of macro algae, or seaweeds, is cosmopolitan in distribution, and has been reported from the artic, temperate and tropical regions of the world. They occur in intertidal and shallow subtidal zones on hard bottoms, attached to surfaces, but can also drift with prevailing water movements. They are usually deep red, maroon, or purplish, but may also be orange or green in coloration. Several species display rounded and strap-shaped branches which start from a small holdfast (a root-like structure). In some species, the entire plant consists of slender, rounded branches that constrict slightly at their point of attachment. In others, main branches are strap-shaped and branchlets are strap-shaped or rounded in cross section. The branches can reach up to 1 foot in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This group of macro algae has a holdfast (a root-like structure) with which it can attach to clam bags and cover netting. They can also drift, meaning they float with prevailing currents, and can be found to “roll” on the bottom. They can become a problem at lease areas with limited flow, such as those located in lagoons, sounds and harbors, and at high water temperatures. When they die and decompose on top of clam bags, an anoxic (no oxygen) layer can be created, resulting in clam mortalities.
- FOE
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Inspect bags to determine extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited flow and when water temperatures are high. If fouling over the bags is extensive, then it must be removed. Some clam growers actually use custom-designed “push” nets, operated from their boats to remove the drift algae. Fouled cover netting could be removed and clean cover netting replaced over bags.
Rolling Moss, Drift Algae
Description
This alga is found in Florida and the Antilles on shell fragments, sand plains, or tangled in seagrass beds to 90 feet deep. It can be purple, pink, rose-red, or brown in color. The branches are cylindrical, irregularly alternate, and may appear to have knobs between branchlets. It can reach heights of up to 6 feet.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
This macro algae can drift, meaning it floats with prevailing currents, and can be found to “roll” on the bottom. It also has a holdfast (a root-like structure) with which it can attach to clam bags and cover netting. It can become a problem at lease areas with limited flow, such as those located in lagoons, sounds and harbors, and at high water temperatures. When it dies and decomposes on top of clam bags, it can create an anoxic (no oxygen) layer, resulting in clam mortalities.
- FOE
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Inspect bags to determine extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited flow and when water temperatures are high. If fouling over the bags is extensive, then it must be removed. Some clam growers actually use custom-designed “push” nets, operated from their boats to move the algae. Fouled cover netting could be removed and clean cover netting replaced over bags.
Rolling Moss, Drift Algae
Description
This tough, cartilaginous group of algae can be highly variable but most forms are bushy and dark red to green-brown in color. Branches are cylindrical and branchlets may appear to have knobby ends. These algae are common throughout Florida, the Bahamas, and the Caribbean. During certain times of the year, they can form dense drift mats on the bottom. Clumps can reach 6 to12 inches in diameter.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
These macro algae can drift, meaning they float with prevailing currents, and can be found to “roll” on the bottom. They also have a holdfast (a root-like structure) with which they can attach to clam bags and cover netting. They can become a problem at lease areas with limited flow, such as those located in lagoons, sounds and harbors, and at high water temperatures. When they die and decompose on top of clam bags, they can create an anoxic (no oxygen) layer, resulting in clam mortalities.
- FOE
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Inspect bags to determine extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited flow and when water temperatures are high. If fouling over the bags is extensive, then it must be removed. Some clam growers actually use custom-designed “push” nets, operated from their boats to move the algae. Fouled cover netting could be removed and clean cover netting replaced over bags.
Colorful Sea Whip
Description
Colorful sea whips grow on shelly bottoms in bays and tidal creeks, but can also be found on docks and oyster reefs. They may be purple, white, orange, yellow, or red. Colonies attach to hard substrates with a tough holdfast (a root-like structure). Undisturbed colonies expand small white polyps from the stem and branches. The springy branches have an internal skeleton that looks like a black or brown wire. Colorful sea whips grow to 24 inches in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The colorful sea whip is a filter feeder and, therefore, competes with clams for the same types of food (micro algae). It attaches to clam culture bags and other hard substrates with a tough tenacious holdfast.
- FOE
- Competitor
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Colorful sea whips can be difficult to impossible to remove from bags. However, they do not occur in high densities and consist of a few springy branches. Therefore, they pose little problem as fouling organisms. Some growers believe that the presence of sea whips on a culture bag indicates “good clam production.”
Feather Hydroid
Description
Feather hydroids are abundant fouling organisms in high salinity areas, especially in summer and fall. They particularly like moderate to strong water flow. Branches are arranged on either side of a central branch, resembling a feather. Stems are black and the polyps are pinkish-white. Polyps are cone-shaped, with a whorl of long tentacles at the base and whorls of short tentacles at the top. Feather hydroids reach 8 inches in height.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The feather hydroid is a filter feeder and, therefore, competes with clams for the same types of food (micro algae). It can also be a fouling nuisance on clam bags. If fouling is extensive enough to restrict water flow into the bags, clams may suffocate, especially at high water temperatures.
- FOE
- Competitor
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Growers should inspect culture bags to determine the extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited tidal exchange. Clumps can be manually removed by hand or with a brush and will not reattach. Extensively fouled cover netting can be replaced with clean netting.
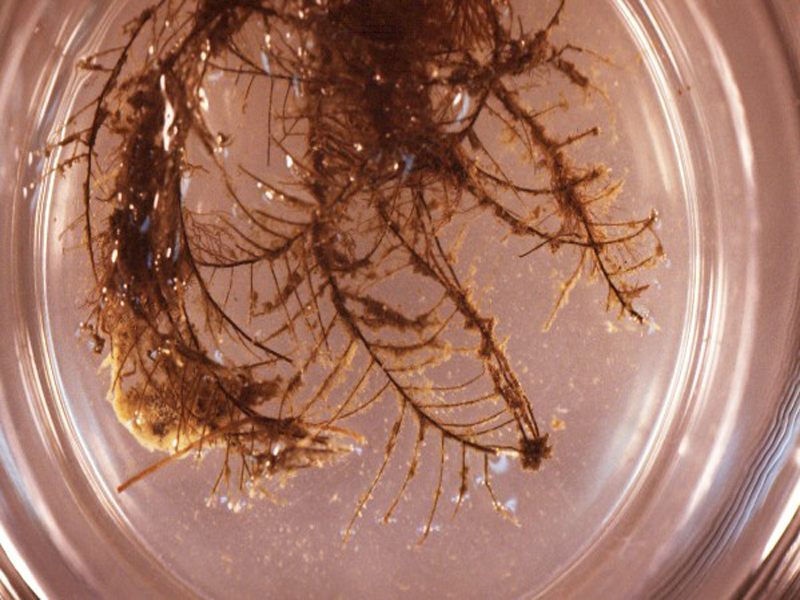
Taxonomy
- Kingdom:Animalia
- Phylum: CNIDARIA
- SubPhylum:
- Class: Hydrozoa
- Order: Anthoathecatae
- Family: Pennariidae
- Genus: Pennaria
- Species: disticha
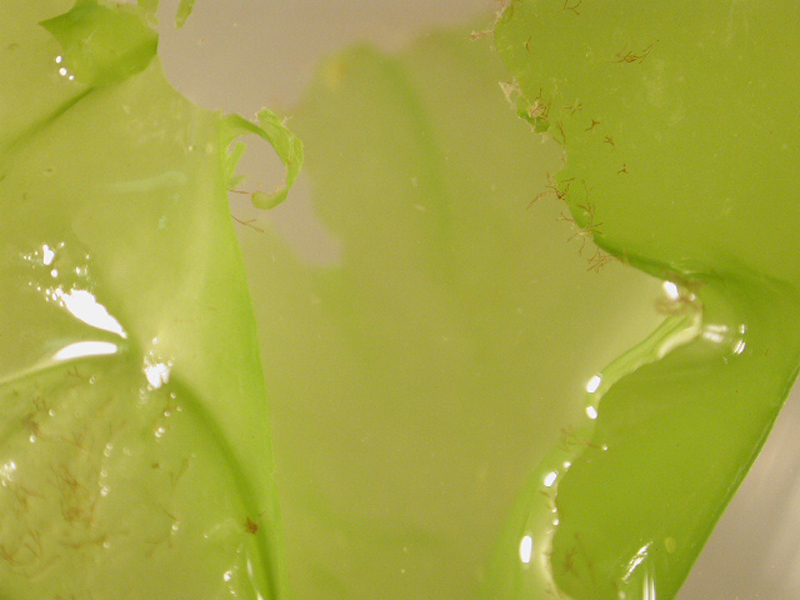
Sea Lettuce
Description
Sea lettuce has one to several wrinkled, broad, and flat blades arising from a basal holdfast and is one of the best-known seaweeds. It can also be found free-floating in tidal shallows. This bright green macro algae can reach 10 feet in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
Sea lettuce has a holdfast (a root-like structure) with which it can attach to clam bags and cover netting. It can also be a drift macro algae, meaning it can float and move with prevailing currents. It can become a problem at lease areas with limited flow, such as those located in lagoons, sounds and harbors, and at high water temperatures. When it dies and decomposes on top of clam bags, it can create an anoxic (no oxygen) layer, resulting in clam mortalities.
- FOE
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Inspect bags to determine extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited flow and when water temperatures are high. If fouling over the bags is extensive, then it must be removed. Some clam growers actually use custom-designed “push” nets, operated from their boats to remove drift algae. Fouled cover netting could be removed and clean cover netting replaced over bags.
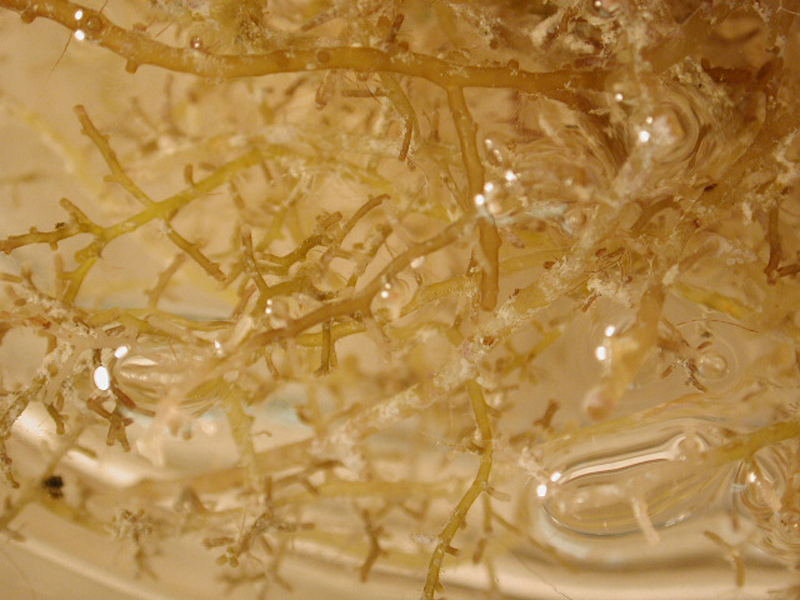
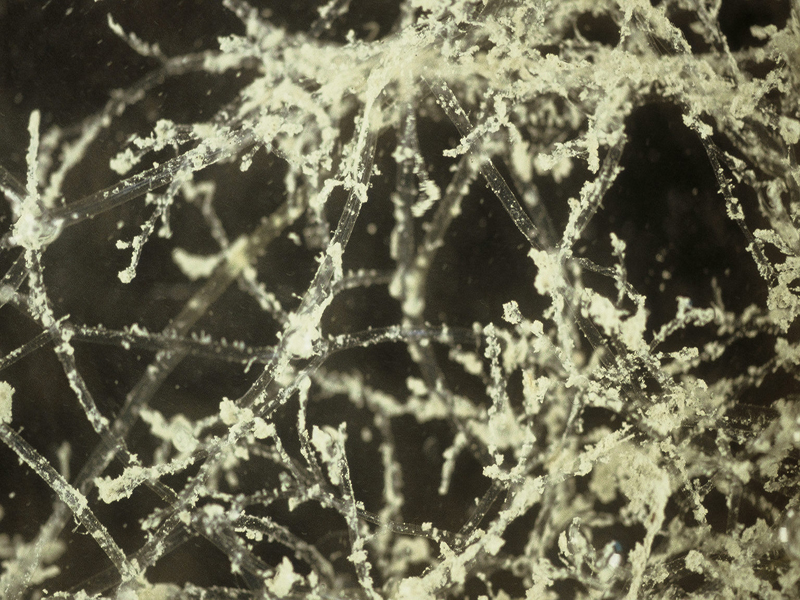
Straw Bryozoan
Description
The straw bryozoan occurs in quiet waters in deep tidal creeks or harbors, but can also be found intertidally. Individual zooids (individuals in a colony arising through asexual reproduction) are found in two rows on each side of the stem and branches. The irregular branches are soft and flaccid, resembling transparent oriental noodles. The straw bryozoan may exceed 12 inches in length.
What Are The Effects On Clams?
The straw bryozoan is a filter feeder and therefore competes with clams for the same types of food (micro algae). It can also be a fouling nuisance on clam bags. If fouling is extensive enough to restrict water flow into the bags, clams may suffocate, especially at high water temperatures.
- FOE
- Competitor
- Fouler
What Can A Clam Farmer Do?
Growers should inspect culture bags to determine the extent of fouling, particularly at lease sites with limited tidal exchange. Clumps can be manually removed by hand or with a brush and will not reattach. Extensively fouled cover netting can be replaced with clean netting.